Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development
The rapid advancement of technology has underscored the fundamental role that printed circuit boards (PCBs) play in modern electronics development. As the backbone of nearly all electronic devices, PCBs enable seamless electrical connections and support the integration of complex circuitry. According to recent industry reports, the global PCB market is projected to reach approximately $80 billion by 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.6% from 2020. This growth is primarily driven by the increasing demand for consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and advanced telecommunications systems.
Furthermore, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has placed even greater emphasis on the need for high-quality printed circuit boards, as billions of connected devices require robust and efficient electronic solutions. An analysis by MarketsandMarkets notes that the IoT sector alone is expected to generate substantial demand for PCBs, as more industries seek to incorporate smart technologies. Therefore, understanding the pivotal role of printed circuit boards in electronic development not only highlights their significance but also emphasizes the necessity for innovation and quality in PCB manufacturing to support future technological advancements.
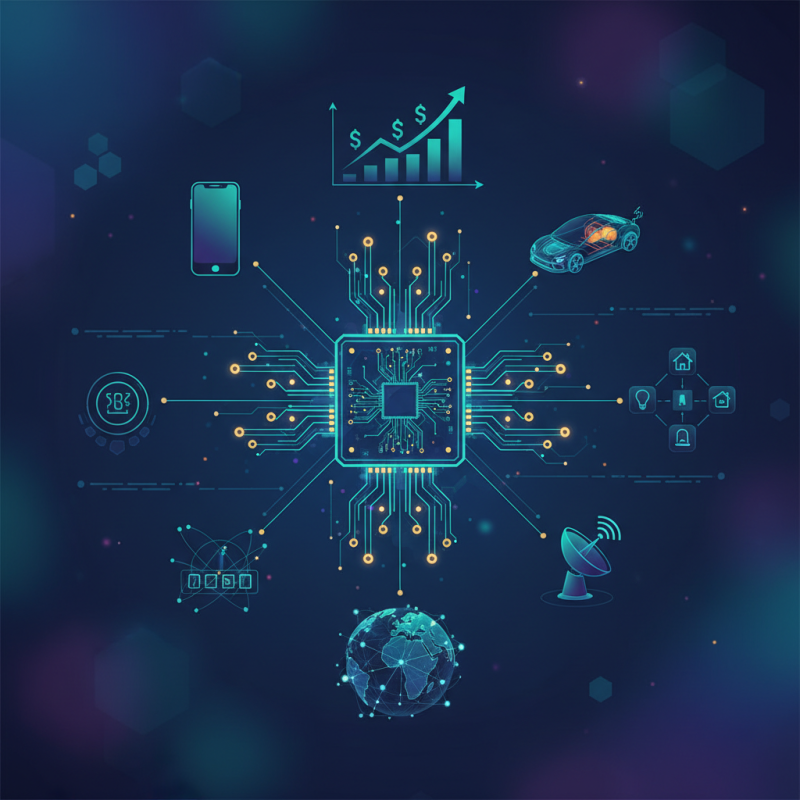

Importance of Printed Circuit Boards in Electronics
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) serve as the backbone of modern electronic devices, providing a structured way to connect various electronic components. Their importance in electronics stems from their role in facilitating reliable electrical connections while minimizing physical space. Unlike traditional wiring methods, which can lead to tangled connections and increased chances of failures, PCBs utilize a flat, rigid board composed of insulating material with conductive pathways etched into it. This design not only allows for a compact arrangement of components but significantly enhances the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
Moreover, PCBs play a crucial role in the scalability of electronic systems. As technology advances, the need for more complex circuits increases. PCBs can be designed and manufactured to meet specific requirements for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. With the advent of surface mount technology, components can now be placed on both sides of the PCB, further optimizing space and efficiency. This adaptability makes PCBs essential for innovations in electronics, enabling designers to create smaller, more powerful devices that meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market.
Evolution of Printed Circuit Boards in Modern Technology
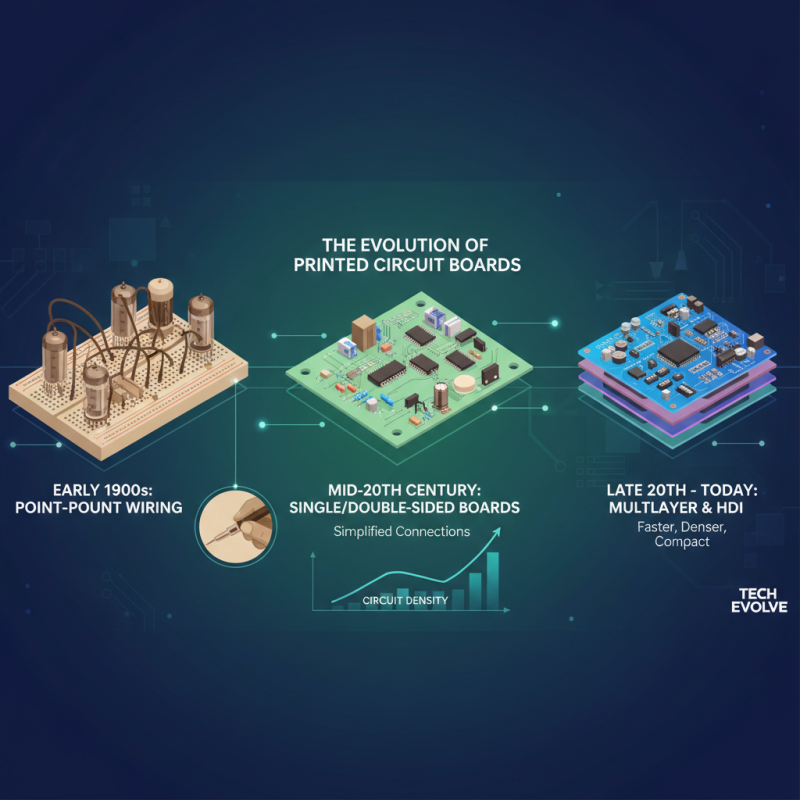
The evolution of printed circuit boards (PCBs) has been nothing short of revolutionary, marking a significant milestone in the development of modern technology. Initially, the concept of PCBs emerged in the early 20th century, primarily as a means to simplify the connection of electronic components. As technology progressed, so did the designs and materials used in PCBs. From rudimentary point-to-point wiring, engineers began adopting multilayer boards and complex layouts that allowed for faster signal transmission, reduced interference, and higher circuitry density.
In recent years, the integration of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques has propelled PCBs into the forefront of electronic innovation. This includes the development of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs that cater to the growing demand for compact and lightweight devices in sectors such as wearables and mobile technology. Furthermore, advancements in surface mount technology (SMT) have enabled the creation of smaller components that can be densely packed, resulting in highly efficient circuit designs. As a result, PCBs are now essential to a vast array of applications, from consumer electronics to aerospace systems, showcasing their vital role in driving the future of technology.
Key Components and Functions of Printed Circuit Boards
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) play a critical role in modern electronics, serving as the backbone for various electronic devices. These boards are composed of a non-conductive substrate, typically made of fiberglass, which supports conductive pathways etched from copper. These pathways facilitate the electrical connection between different electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. By allowing for compact arrangements and efficient routing of signals and power, PCBs enable the miniaturization of electronic devices, making them lighter and more efficient.
In addition to physical support and connectivity, PCBs serve as a framework for circuit design, allowing engineers to create complex layouts that optimize space and performance. The meticulous arrangement on a PCB reduces electromagnetic interference, enhances signal integrity, and improves thermal management, crucial for the reliability of electronic systems. Furthermore, advances in PCB technology, such as multilayer boards and flexible circuits, have expanded the possibilities for innovative designs in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and medical devices, ensuring that they meet the evolving demands of modern technology.
Why Printed Circuit Boards Are Essential for Modern Electronics Development - Key Components and Functions of Printed Circuit Boards
| Component | Function | Material | Thickness (mm) | Common Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper Traces | Conduct electricity between components | Copper | 0.035 | Consumer Electronics |
| Substrate | Support and insulate copper traces | FR-4 | 1.6 | Computers, Smartphones |
| Solder Mask | Prevent solder from bridging | Epoxy resin | NA | All electronic devices |
| Silkscreen | Label and identify components | White ink | NA | All electronic devices |
Challenges in PCB Design and Manufacturing
The design and manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) present several challenges that can impact the overall reliability and performance of electronic devices. According to a report by the IPC, nearly 60% of PCB manufacturers reported that achieving optimal yield rates continues to be a significant issue. This is largely due to the increasing complexity of designs, which often involve densely packed components and multilayer configurations. As the industry pushes for smaller, lighter, and more powerful devices, engineers face the daunting task of fitting more functionality into a limited space without compromising quality.
Moreover, the rapid pace of technological advancement in electronics requires PCB designs to adapt quickly, which can strain manufacturing processes. The 2022 Global PCB Industry Report highlighted that nearly 45% of manufacturers experience delays in production due to design errors or the need for frequent revisions. This not only increases costs but also affects time-to-market, making it crucial for designers to adopt more robust validation methods, such as simulation software and automated testing tools, to identify potential issues before manufacturing begins. As the demand for high-performance electronics grows, overcoming these design and manufacturing challenges becomes essential for sustaining innovation in the industry.
Challenges in PCB Design and Manufacturing
Future Trends in Printed Circuit Board Development
The future of printed circuit board (PCB) development is poised for significant transformation as technological advancements continue to evolve. One of the most notable trends is the push towards miniaturization and increased functionality. As devices become smaller, the demand for PCBs that can support complex functions within a compact space has surged. Innovations in materials, such as flexible and high-density interconnects, enable engineers to design boards that not only save space but also enhance performance by supporting higher frequencies and greater power efficiency.
Another emerging trend in PCB development is the integration of smart technology, paving the way for the Internet of Things (IoT). As more devices are interconnected, PCBs must support communication protocols and power management systems. The incorporation of sensors and embedded functionalities within the PCB itself will facilitate real-time data exchange and monitoring, significantly streamlining the operation of smart devices.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the design and manufacturing of PCBs. The industry is leaning towards environmentally friendly materials and processes, aiming to reduce waste and improve recyclability. This shift reflects broader societal demands for more responsible manufacturing practices, ensuring that the future of electronics aligns with ecological considerations.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 10 Innovations in PCB Electronics You Must Know
-

Exploring Innovations in Printed Circuit Board Technology at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-
How to Choose the Best PCB Fabrication Partner for Global Supply Chain Success
-

Common Issues Faced in High Density PCB Circuit Design
-

2025 Top 5 PCB Printing Innovations Transforming the Electronics Industry
-
2025 Top 10 Trends in Printed Circuit Board Assembly: Industry Growth & Innovations
