Top Factors to Consider for PCB Fabrication in Electronics Manufacturing
In the rapidly evolving field of electronics manufacturing, the significance of PCB fabrication cannot be overstated. Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) serve as the backbone of electronic devices, providing the necessary connections and support for components to function effectively. As technology advances, the complexity and demand for high-quality PCBs are increasing, making it essential for manufacturers to consider a range of crucial factors during the fabrication process.
Effective PCB fabrication encompasses various elements, including materials selection, manufacturing techniques, and design specifications. Each factor plays a pivotal role in determining the performance, reliability, and overall success of the final electronic product. By understanding and addressing these considerations, manufacturers can optimize production processes, minimize costs, and enhance product quality. This introduction serves as a foundation to explore the key aspects that influence PCB fabrication, laying the groundwork for a deeper discussion on best practices and critical challenges faced in the electronics manufacturing industry.

Key Considerations for Material Selection in PCB Fabrication
When considering materials for PCB fabrication, the selection process significantly impacts the performance, durability, and overall cost of the final product. One crucial factor is the dielectric constant of the materials used. For instance, high-frequency applications typically require substrates with lower dielectric constants, such as Rogers materials, which are known for their excellent thermal stability and electrical performance. According to a report by IPC, approximately 25% of PCB failures in the field can be traced back to poor material selection, underscoring the critical nature of choosing the right substrate for specific applications.
 Another important consideration is thermal conductivity. As electronic devices become more compact and power-intensive, managing heat dissipation becomes pivotal. Materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum or certain advanced ceramics, can enhance heat transfer and prevent overheating. A study by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) highlights that using appropriate materials can enhance the lifespan of PCBs by up to 50%, emphasizing the necessity for engineers to prioritize material selection that aligns with the thermal demands of their applications. Balancing these properties against cost and manufacturability remains a key challenge in PCB design and production, making informed material choices indispensable for achieving optimal performance in electronic systems.
Another important consideration is thermal conductivity. As electronic devices become more compact and power-intensive, managing heat dissipation becomes pivotal. Materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum or certain advanced ceramics, can enhance heat transfer and prevent overheating. A study by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) highlights that using appropriate materials can enhance the lifespan of PCBs by up to 50%, emphasizing the necessity for engineers to prioritize material selection that aligns with the thermal demands of their applications. Balancing these properties against cost and manufacturability remains a key challenge in PCB design and production, making informed material choices indispensable for achieving optimal performance in electronic systems.
Understanding PCB Layer Count and Its Impact on Design Complexity
When it comes to PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design, the layer count is a critical factor that directly influences the complexity of the project. As electronic devices become increasingly sophisticated, the demand for compact, multilayer PCBs has surged. Each additional layer not only increases the physical space for circuit paths but also significantly enhances the board's capacity to accommodate more components and intricate designs. This complexity allows for advanced functions in devices, such as faster processing speeds and improved signal integrity.
However, a higher layer count also introduces various challenges. Designers must carefully consider thermal management, electrical performance, and manufacturing capabilities. Each layer requires precise alignment and sufficient spacing to prevent issues like crosstalk and signal interference. Moreover, increasing the number of layers can lead to higher production costs and longer fabrication times. Therefore, striking the right balance between layer count and design requirements is essential for optimizing both performance and manufacturability in PCB fabrication. Understanding these dynamics allows engineers to make informed decisions that align with both functional specifications and production limitations.
Importance of Manufacturing Tolerances and Specifications in PCBs
When it comes to PCB fabrication in electronics manufacturing, the importance of manufacturing tolerances and specifications cannot be overstated. These factors determine the overall functionality, reliability, and performance of the final product. High precision in tolerances ensures that the components fit together perfectly, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and performance in intricate electronic designs. Specifications such as trace widths, spacing, and layer count play a vital role in determining the potential applications and capabilities of the PCB.
Tips: When defining tolerances, it's essential to collaborate closely with your engineering team to understand the specific requirements of your product. This collaboration can help avoid common pitfalls and ensure that the PCB meets both electrical and physical requirements. Additionally, consider implementing advanced measuring techniques during the fabrication process to catch any discrepancies early and reduce the need for costly revisions later on.
Understanding the implications of various specifications on manufacturing processes is equally crucial. For instance, tighter specifications may lead to increased production costs and longer lead times. It's essential to strike a balance between quality and cost-effectiveness. Tips: Always communicate your project goals clearly with fabricators and stay updated on technological advancements that may help meet your specifications without sacrificing budget or timeline. This proactive approach will ensure smoother project execution and a successful final product.
Exploring the Role of Surface Finish Options in PCB Performance
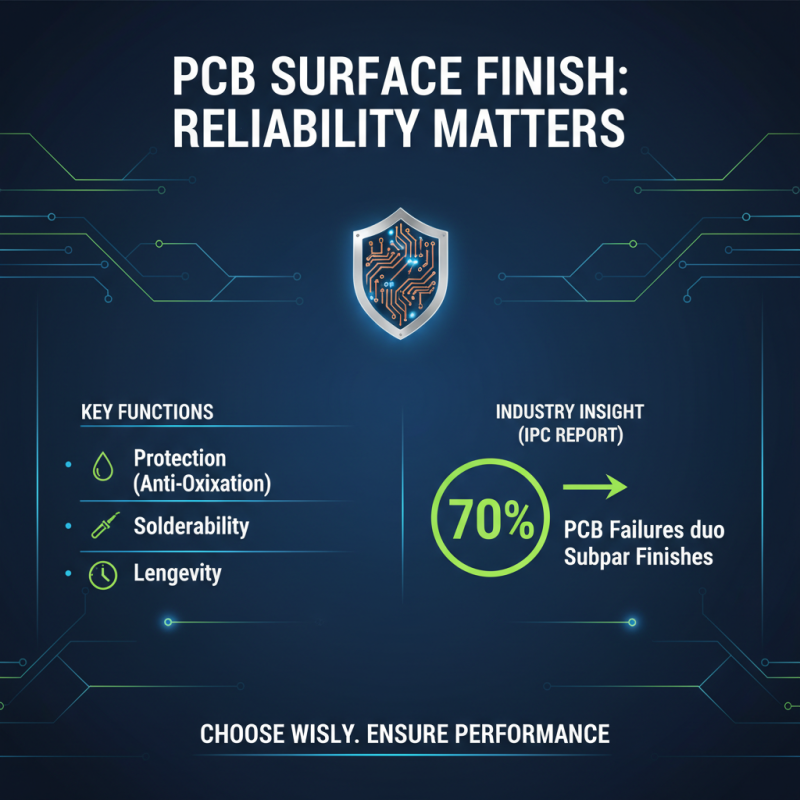
When it comes to PCB (Printed Circuit Board) fabrication, the choice of surface finish can significantly influence the overall performance and reliability of the final product. Surface finishes protect the copper traces on PCBs from oxidation and corrosion, enhance solderability, and contribute to the board's longevity. According to a recent industry report by IPC, nearly 70% of PCB failures can be attributed to subpar surface finish choices, highlighting the importance of selecting the right option based on specific application needs.
Different surface finishes come with their own sets of advantages and limitations. For example, ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) is widely favored for its excellent corrosion resistance and flatness, making it ideal for high-frequency applications. However, it also has a higher production cost. In contrast, HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), while cost-effective and suitable for many standard applications, may not perform as well in terms of thermal stability and fine-pitch soldering. Industry data indicates that approximately 35% of designs that require high-density interconnections are moving towards lead-free finishes, driven by both regulatory requirements and performance demands.
Furthermore, the choice of surface finish can affect assembly processes and the compatibility of components. For instance, surface finishes with a lower solderability might require additional processes like the use of soldering aids. Statistical analyses suggest that 40% of manufacturing delays stem from surface finish-related issues, emphasizing the need for careful consideration at the early design stages. By aligning surface finish options with the specific needs of the application, manufacturers can improve yield rates and reduce the risk of field failures in their electronic products.
Evaluating Cost-Efficiency and Lead Times in PCB Production Processes
When evaluating cost-efficiency and lead times in PCB production processes, it is crucial to understand the intricate balance between quality, speed, and price. The selection of materials and manufacturing techniques directly impacts both the overall cost and the timeline of PCB fabrication. For instance, premium materials may increase the initial costs but can lead to better performance and longevity, thus offering long-term savings. On the other hand, opting for cost-effective solutions may accelerate production but could compromise the quality, potentially resulting in higher failure rates and increased rework costs down the line.
Another significant aspect to consider is the production scale and complexity of the PCB design. High-volume orders often benefit from reduced per-unit costs, but the initial setup and lead times can be lengthy. Conversely, low-volume or custom designs might require more extensive engineering efforts, leading to increased expenses and longer lead times.
Manufacturers must assess their specific needs and market demands to optimize their production strategies. Streamlining operations, utilizing automated manufacturing processes, and implementing effective supply chain management can significantly enhance both cost efficiency and lead times, ensuring a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving electronics market.
Related Posts
-

The Future of Smart PCB Board Technology in Electronics
-

10 Essential PCB Printing Techniques You Need to Know
-
Essential Checklist for Choosing the Best PCB Fabrication Services Based on Industry Standards
-
Ultimate Checklist for Selecting the Best PCB Fabrication Services Worldwide
-

Understanding the Future of Printed Circuit Board Innovations in Technology
-
The Ultimate Guide to PCB Fabrication: Navigating the 2023 Industry Landscape and Beyond
