Why Are PCB Circuit Boards Essential in Modern Electronics?
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, the role of PCB circuit boards cannot be overstated. According to a recent report by the IPC, the global PCB market is projected to reach $80 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the expanding demand for electronics in various sectors, including automotive, telecommunications, and consumer gadgets. "Without PCB circuit boards, modern technology would simply not function," says Dr. Emily Robbins, a renowned expert in electronic manufacturing.
The complexity of modern devices relies heavily on advanced PCB circuit board designs. These boards act as the backbone of electronic systems, linking components and facilitating communication. As innovations continue, boards are becoming more intricate, supporting higher densities and speeds. Yet, the industry faces challenges. Issues such as supply chain disruptions and material shortages are frequent. These obstacles highlight the need for resilience and adaptability, prompting industry leaders to rethink strategies.
Despite the advancements, not all PCB circuit boards are equal in quality. Variations exist that can significantly impact performance. As Dr. Robbins notes, "Not every PCB is designed with the end-user in mind." This raises an important consideration for manufacturers. Balancing cost with performance is crucial for success in this vibrant market.
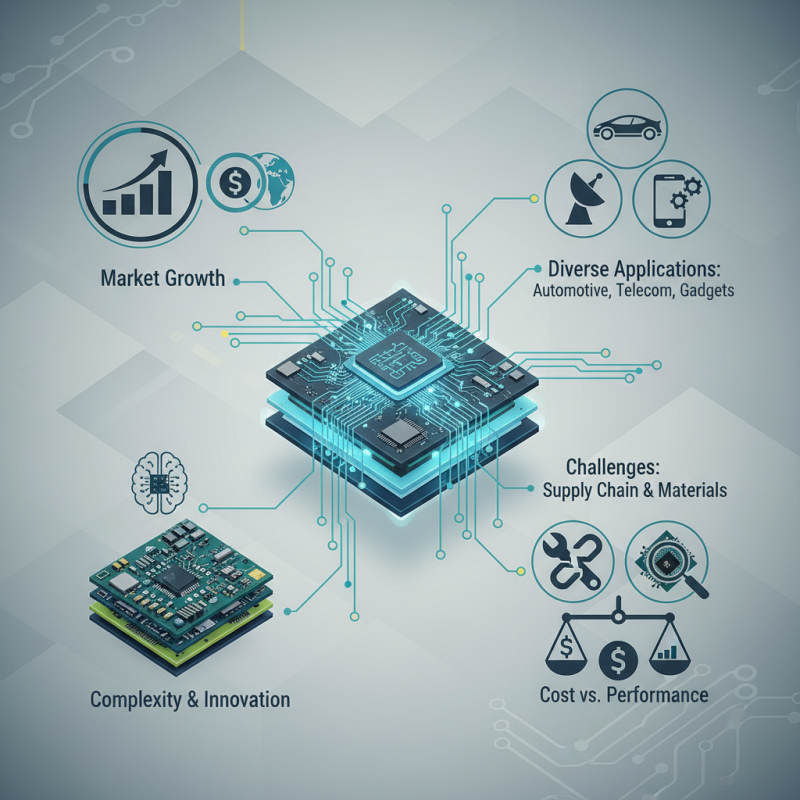
The Role of PCB Circuit Boards in Modern Electronics
PCB circuit boards play a crucial role in today’s electronic devices. They serve as the backbone of various technologies. Each board connects components, ensuring efficient communication. Without them, modern devices would struggle to function seamlessly.
The complexity of electronics relies heavily on PCBs. They house intricate pathways that allow signals to travel. This connection isn’t just about functionality; it’s about precision. Errors in design often lead to malfunctions. Even a tiny flaw can render a device useless. Engineers constantly refine these boards to meet ever-evolving standards.
Yet, challenges persist in PCB manufacturing. Balancing cost-effectiveness with quality is difficult. Many overlook the impact of materials used. Sustainable options are rising, but they often come with trade-offs. These decisions shape the future of electronics. Testing remains vital, as failures can occur in unexpected ways. The journey of improvement is ongoing, reflecting the intricate relationship between design and real-world application.
The Importance of PCB Circuit Boards in Modern Electronics
Key Components and Materials Used in PCB Manufacturing
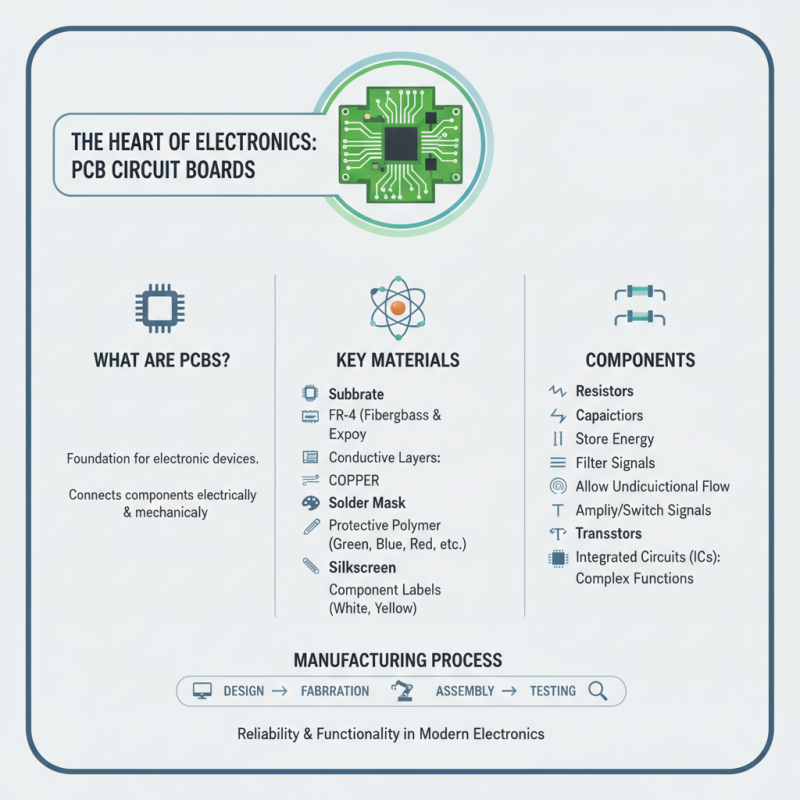
PCB circuit boards are vital in today's electronics. They serve as the foundation for a myriad of devices. The manufacturing of PCBs involves various components and materials that enhance their functionality and reliability.
Key materials used in PCB manufacturing include copper, which is essential for circuit pathways. According to market research, the global PCB market is projected to reach about $77 billion by 2026. This surge emphasizes the importance of high-quality materials. Additionally, substrates like FR-4, made from epoxy fiberglass, are widely used for their durability and electrical insulating properties. Recent studies highlight that about 60% of all PCB production utilizes this substrate.
However, not every manufacturing process is flawless. Issues such as delamination or poor adhesion can arise. These defects may lead to significant failures in electronic devices. Continuous improvements and innovations in material science are necessary. Manufacturers must evaluate their processes regularly to ensure product integrity. The balance between cost and quality remains a challenge worth addressing.
Advantages of PCB Circuit Boards Over Traditional Wiring Methods
PCB circuit boards revolutionized electronics. They offer numerous advantages over traditional wiring methods. First, they allow for compact designs. This results in smaller, lighter devices. Complex circuits fit onto a single board, reducing space.
Moreover, PCBs provide enhanced reliability. Connections are soldered directly, minimizing the risk of loose wires. This leads to fewer failures in electronic devices. The durability of PCBs is also notable; they withstand vibrations and heat better than wires.
Tips for choosing PCB designs: First, consider the layout carefully. You want to minimize the number of layers. More layers can complicate manufacturing. Also, be mindful of the material choice. Different materials react differently under stress. Testing is crucial. Even a small design flaw can lead to massive performance issues. Reflecting on these details can lead to better designs.
Applications of PCB Circuit Boards Across Various Industries

Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) serve as the backbone of modern electronics. Their applications span various industries, showcasing their versatility and importance. In the automotive sector, for example, PCBs power advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment systems. According to a report by Research and Markets, the automotive PCB market is expected to grow significantly, anticipated to reach $19.5 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the increasing demand for smart vehicles.
In the telecommunications industry, PCBs are integral to smartphones and networking equipment. With 5G technology emerging, the need for high-frequency PCBs is critical. The global PCB market in telecommunications is projected to see a substantial CAGR of 4.3% from 2021 to 2026. However, the complexity of these designs poses challenges in manufacturing. Higher frequencies can lead to signal integrity issues. This requires careful engineering and testing.
Medical devices also heavily rely on PCBs. These boards are found in diagnostic equipment, patient monitoring systems, and imaging devices. According to a study by the Global Industry Analysts, the medical PCB market is likely to reach $11.6 billion by 2027. The sensitivity of medical applications demands flawless manufacturing. Any defects can have severe implications for patients. There may still be gaps in achieving 100% reliability, highlighting an area for improvement in the industry.
Future Trends in PCB Technology and Its Impact on Electronics
The evolution of PCB technology drives the electronics industry forward. As devices become smaller, the demand for efficient circuit boards increases. Miniaturization challenges designers to create compact layouts without sacrificing performance. This requires innovative materials and advanced fabrication techniques.
The rise of flexible PCBs is one significant trend. These boards allow for unique designs that bend and conform to various shapes. This flexibility leads to emerging applications in wearables and IoT devices. However, there are challenges. Striking a balance between durability and flexibility is crucial.
Another trend is the shift towards environmentally friendly materials. Traditional processes can harm the environment. New methods aim to reduce waste and energy consumption. Nevertheless, these sustainable solutions often come with higher costs and complex manufacturing processes. Further exploration is needed to find scalable solutions.
Why Are PCB Circuit Boards Essential in Modern Electronics? - Future Trends in PCB Technology and Its Impact on Electronics
| Technology Dimension | Description | Impact on Electronics | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Density Interconnect (HDI) | Allows for more connections in a smaller area | Enables compact electronic devices with enhanced performance | Increased usage in portable and wearable electronics |
| Flexible PCBs | PCB that can bend and flex | Enhances design options for various electronic products | Growth in the medical devices and automotive sectors |
| Multilayer PCBs | PCB with multiple layers for complex circuits | Supports intricate electronic devices and applications | Future innovations in smartphones and IoT devices |
| Embedded Components | Components such as resistors and capacitors built into the PCB | Reduces space and assembly costs | More widespread integration in compact devices |
| Environmental Considerations | Use of sustainable materials and recycling processes | Promotes eco-friendly electronic manufacturing | Increased focus on green technologies in the industry |
Related Posts
-
Ultimate Checklist for Selecting the Best PCB Fabrication Services Worldwide
-
Essential Checklist for Choosing the Best PCB Fabrication Services Based on Industry Standards
-
The Ultimate Guide to PCB Fabrication: Navigating the 2023 Industry Landscape and Beyond
-

The Future of Smart PCB Board Technology in Electronics
-

Understanding PCB Printing Techniques and Their Impact on Modern Electronics Efficiency
-

10 Essential PCB Printing Techniques You Need to Know
